Following recent cybersecurity events, we’ve seen a significant increase in inquiries from our customers and partners about software update reliability and our release strategy. We’re providing an overview of our software release process at Bitdefender to address growing industry concerns. This process is designed to do everything we can to help minimize the risk of disruptions to your business.
1: Development and QA Process
Our development process prioritizes quality and reliability from the very beginning. The Software Development Lifecycle (SDLC) integrates best practices at every phase to prevent software issues from reaching the final product. Through comprehensive testing and continuous improvement, we ensure products meet the highest standards of performance and functionality. Before any update reaches your endpoints, it undergoes a series of rigorous manual and automated tests.
- Automated Testing – Nearly all (over 90%) of possible scenarios are covered by our robust suite of automated tests. This extensive automation allows us to efficiently re-run the entire test suite after minor code changes, ensuring consistent quality throughout development. These automated tests are executed continuously (daily) between releases, not only when manually triggered by engineers.
- Manual Testing – While automation plays a vital role, our skilled QA engineers (separate from the developers) put software through its paces to uncover any issues.
Secure development and rigorous testing are industry standards. At Bitdefender, we follow these practices to ensure the stability and reliability of the GravityZone Platform and all its components.
2: Release Process and Best Practices
Even with the most rigorous QA procedures, unforeseen issues will happen during software updates. To minimize disruptions, we’ve implemented a controlled and closely monitored multi-stage release process for both our cloud console and endpoint agents.
We use our own products and services in-house to thoroughly test their functionality, identify any issues, and ensure they meet high standards before releasing them to our customers. Updates are deployed internally across our entire company, not just engineering, before reaching you. This real-world testing helps us identify any issues before wider release.
Highly sensitive updates, such as major updates of kernel drivers, undergo extended controlled rollouts (sometimes lasting months) with clear communication in the Release Notes to ensure minimal disruption.
Cloud Releases: Gradual Regional Deployment
For cloud updates, we use a gradual regional deployment process. This approach minimizes the potential impact of any unforeseen issues by strategically rolling out updates across multiple regions in phases.
We always start with a “virtual” region comprised of our employees. This controlled environment allows us to identify and resolve potential issues before they impact our customers.
The update is gradually deployed across different regions over a set timeframe. This allows us to identify and address issues that might arise without impacting all users simultaneously.
Endpoint Agents: Staging Updates
For endpoint agent updates, we use a phased rollout strategy. Here’s a breakdown of these stages:
- Super Fast Ring – Updates are always deployed internally before reaching customers. After engineering approves a release update, it is first deployed to all Bitdefender employees for further real-world testing and feedback.
- Fast Ring – After our rigorous internal testing, the update becomes available on the Fast Ring. This program allows our customers to test the update in their environments before it’s widely deployed. By using the Fast Ring, you can help us identify any unforeseen issues or compatibility problems with your specific software or hardware setup.
- We typically keep updates on the Fast Ring for a week. For emergency fixes, the Slow Ring can be updated within 24 hours of the Fast Ring release.
- For critical issues, Slow Ring releases can be delayed or stopped entirely until a new version with the resolved issues is released, restarting the whole release cycle.
- Slow Ring – This option prioritizes stability by receiving updates at a later date. By the time the update reaches the Slow Ring, it has been thoroughly tested internally and by Fast Ring users and any necessary adjustments have been made.
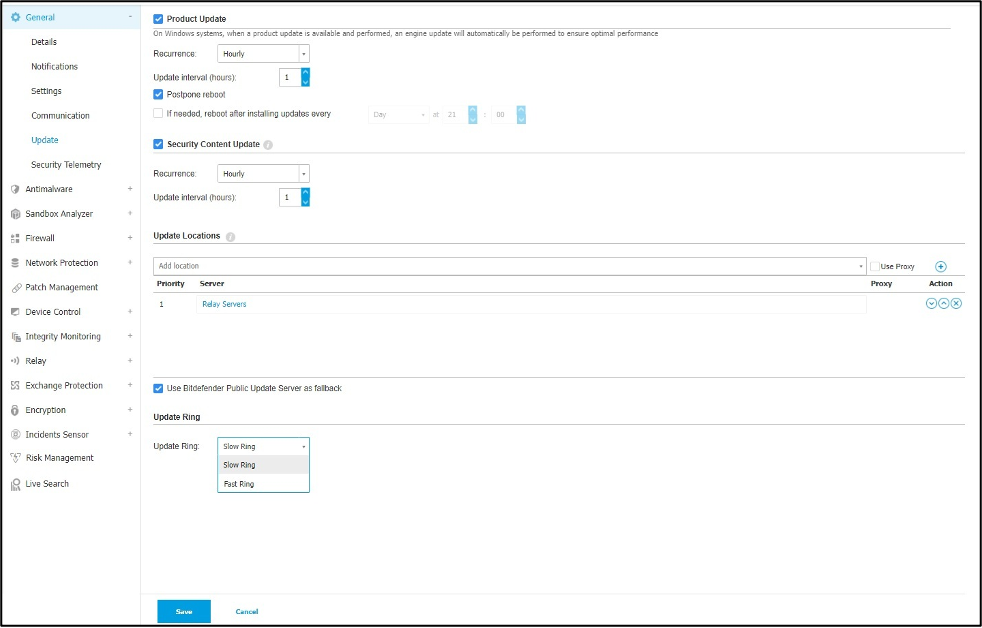
Easily assign endpoints to Fast or Slow Ring for controlled updates.
Identifying and fixing issues early in the Super Fast Ring and Fast Ring stages has yielded a clear benefit in 2024: there haven’t been any rollbacks needed for Slow Ring updates.
Conclusion
We’ve explained how Bitdefender carefully rolls out updates in stages to keep operations running smoothly for everyone – but keeping systems safe is a team effort. Here are some of the best practices to avoid unnecessary disruptions:
- Use Both Rings: We recommend using both Fast and Slow Rings.
- Test Early with Fast Ring: Put a small number of non-critical machines on the Fast Ring. This way, you can catch any compatibility issues with your specific setup before everyone gets the update.
- Stay Stable with Slow Ring: Keep most of your machines on the Slow Ring. They’ll benefit from the extra testing done by the Fast Ring users, making unexpected problems less likely.
- Separate Rings, Separate Rules: Set up different policies for Fast Ring and Slow Ring updates. This gives you more control over when updates happen and lets you target specific machines.
- Test Like a User: Many IT teams perform internal testing in controlled environments, often using dedicated test setups with separate domains. An additional phase called User Acceptance Testing (UAT) is crucial to ensure a smooth rollout. During UAT, regular end users test the Fast Ring update in your actual production network during their regular work hours and workloads.
- Review Release Notes: Before deploying any update, especially on the Slow Ring, take a few minutes to review the accompanying release notes. These notes detail the specific changes, bug fixes, and known issues associated with the update.

